Program That Control Cpu Fan Speed
Program That Control Cpu Fan Speed' title='Program That Control Cpu Fan Speed' />1. The program detects a fan sensor chip but setting the speeds via direct fan control has no effect. The successful detection of a fan speed sensor doesnt mean that. Overclocking Wikipedia. Overclocking BIOS setup on an ABIT NF7 S motherboard with an AMD Athlon XP processor. Front side bus FSB frequency external clock has been increased from 1. MHz to 1. 48 MHz, and the CPU clock multiplier factor has been changed from 1. This corresponds to an overclocking of the FSB by 1. CPU by 3. 6. Not to be confused with overclockingmileometerodometerOverclocking is configuration of computer hardware components to operate faster than certified by the original manufacturer, with faster specified as clock frequency in megahertz MHz or gigahertz GHz. Commonly operating voltage is also increased to maintain a components operational stability at accelerated speeds. Semiconductor devices operated at higher frequencies and voltages increase power consumption and heat. An overclocked device may be unreliable or fail completely if the additional heat load is not removed or power delivery components cannot meet increased power demands. Many device warranties state that overclocking andor over specification voids any warranty. OvervieweditThe purpose of overclocking is to gain additional performance from a given component by increasing its operating speed. The CPU fan in my laptop is running too fast. I wish to control the speed manually to my preference, at times. Here is a CPUZ screenshot of my laptop configuration. How to Overclock a CPU. Overclocking a CPU is the process of increasing the clock speed that the CPU operates at. Overclocking has traditionally been the. Gta Vice City Full Version On Pc on this page. Normally, on modern systems, the target of overclocking is increasing the performance of a major chip or subsystem, such as the main processor or graphics controller, but other components, such as system memory RAM or system buses generally on the motherboard, are commonly involved. The trade offs are an increase in power consumption heat and fan noise cooling for the targeted components. Most components are designed with a margin of safety to deal with operating conditions outside of a manufacturers control examples are ambient temperature and fluctuations in operating voltage. Overclocking techniques in general aim to trade this safety margin by setting the device to run in the higher end of the margin, with the understanding that temperature and voltage must be more strictly monitored and controlled by the user. Examples are that operating temperature would need to be more strictly controlled with increased cooling, as the part will be less tolerant of increased temperatures at the higher speeds. Also base operating voltage may be increased to compensate for unexpected voltage drops and to strengthen signalling and timing signals, as low voltage excursions are more likely to cause malfunctions at higher operating speeds. While most modern devices are fairly tolerant of overclocking, all devices have finite limits, generally for any given voltage most parts will have a maximum stable speed where they still operate correctly. Past this speed the device starts giving incorrect results, which can cause malfunctions and sporadic behavior in any system depending on it. While in a PC context the usual result is a system crash, more subtle errors can go undetected, which over a long enough time can give unpleasant surprises such as data corruption incorrectly calculated results, or worse writing to storage incorrectly or the system failing only during certain specific tasks general usage such as internet browsing and word processing appear fine, but any application wanting advanced graphics crashes the system. At this point an increase in operating voltage of a part may allow more headroom for further increases in clock speed, but increased voltage can also significantly increase heat output. At some point there will be a limit imposed by the ability to supply the device with sufficient power, the users ability to cool the part, and the devices own maximum voltage tolerance before it achieves destructive failure. Overzealous use of voltage andor inadequate cooling can rapidly degrade a devices performance to the point of failure, or in extreme cases outright destroy it. The speed gained by overclocking depends largely upon the applications and workloads being run on the system, and what components are being overclocked by the user benchmarks for different purposes are published. UnderclockingeditConversely, the primary goal of underclocking is to reduce power consumption and the resultant heat generation of a device, with the trade offs being lower clock speeds and reductions in performance. Reducing the cooling requirements needed to keep a part at a given operational temperature has knock on benefits such as lowering the number and speed of fans to allow quieter operation, and in mobile devices increase length of battery life per charge. Some manufacturers underclock components of battery powered equipment to improve battery life, or implement systems that detect when a device is operating under battery power and reduce clock frequency accordingly. Underclocking is almost always involved in the latter stages of Undervolting, which seeks to find the highest clock speed that a processor will stably operate at a given voltage. That is, while overclocking seeks to maximize clock speed with temperature and power as constraints, underclocking seeks to find the highest clock speed that a device can reliably operate at a fixed, arbitrary power limit. A given device may operate correctly at its stock speed even when undervolted, in which case underclocking would only be employed after further reductions in voltage finally destabilizes the part. At that point the user would need to determine if last working voltage and speed have satisfactorily lowered power consumption for their needs if not then performance must be sacrificed, a lower clock is chosen the underclock and testing at progressively lower voltages would continue from that point. A lower bound is where the device itself fails to function andor the supporting circuity cannot reliably communicate with the part. Im having this problem too. Sometimes the CPU temp goes high, and the fan kicks in at maximum speed, although there is nothing running 99100 idle in iStat. Multicore processors add an additional layer of complexity to software design. Occasionally that can manifest as only 25 of the CPU being used. Underclocking and undervolting are usually attempted if a system needs to operate silently such as a multimedia player, but if higher performance is desired than is offered by a given processor manufacturers low voltage offerings, then the builder will attempt to take a higher performance desktop part with a higher stock thermal output, and see if the processor will run with lower voltages and speeds within an acceptable performancenoise target for the build. Thus it may give some options to undervoltunderclock a standard voltage processor in a low voltage application either to avoid paying a price premium for an officially certified low voltage version some low power versions are significantly more expensive, and even then are often still slower than their desktop equivalent, or if better performance is required than offered by the low power processors available. Enthusiast cultureeditOverclocking has become more accessible with motherboard makers offering overclocking as a marketing feature on their mainstream product lines. Program That Control Cpu Fan Speed' title='Program That Control Cpu Fan Speed' />Is one of your computer fans loud or making noise Heres how to tell which one it is and how to fix it so your computer doesnt overheat. If youre overclocking your Republic of Gamers PC or ASUS motherboard, then its always good to know the state of your system in terms of fan speed, CPU and. PNG' alt='Program That Control Cpu Fan Speed' title='Program That Control Cpu Fan Speed' />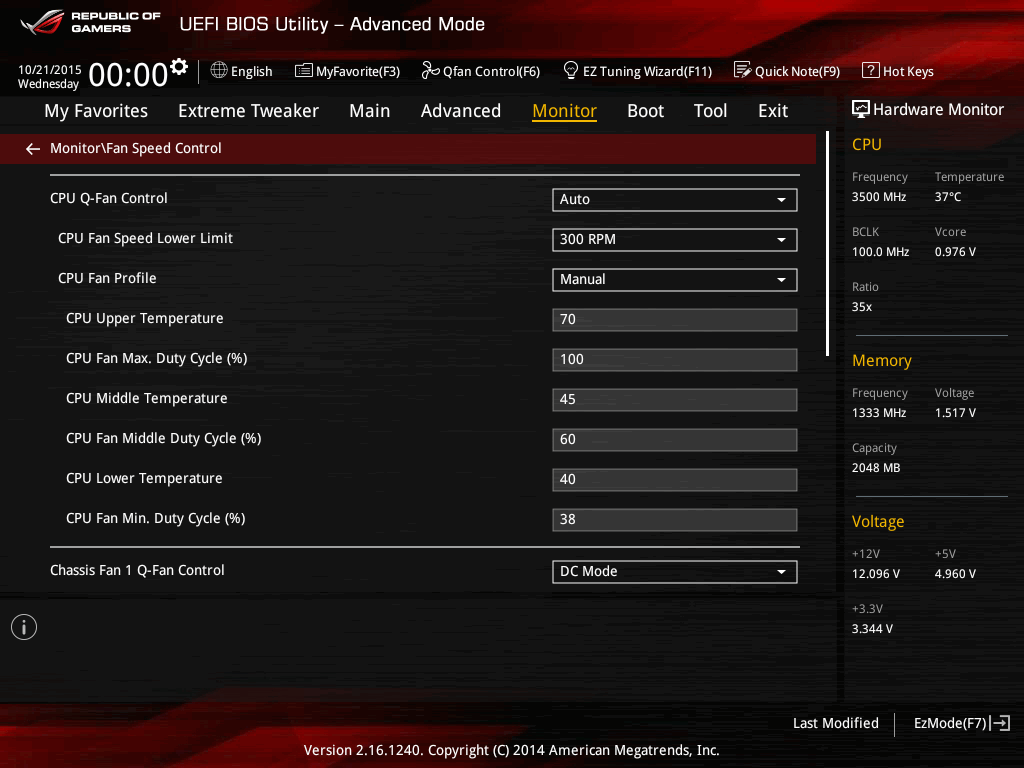 However, the practice is embraced more by enthusiasts than professional users, as overclocking carries a risk of reduced reliability, accuracy and damage to data and equipment. Additionally, most manufacturer warranties and service agreements do not cover overclocked components nor any incidental damages caused by their use. While overclocking can still be an option for increasing personal computing capacity, and thus workflow productivity for professional users, the importance of stability testing components thoroughly before employing them into a production environment cannot be overstated. Overclocking offers several draws for overclocking enthusiasts.
However, the practice is embraced more by enthusiasts than professional users, as overclocking carries a risk of reduced reliability, accuracy and damage to data and equipment. Additionally, most manufacturer warranties and service agreements do not cover overclocked components nor any incidental damages caused by their use. While overclocking can still be an option for increasing personal computing capacity, and thus workflow productivity for professional users, the importance of stability testing components thoroughly before employing them into a production environment cannot be overstated. Overclocking offers several draws for overclocking enthusiasts.